Working Groups & Activities
I. Logical Framework in the Project Design Matrix (PDM)
The Project's purpose is to strengthen research capacity to continuously monitor the multi-drug resistant bacteria, which is expected to contribute in the super goal of preventing the spread of multi-drug resistant bacteria in Vietnam. To achieve the Project's purpose, the Project Design Matrix (PDM) agreed between Vietnam and Japan sets up three outputs:1) research output, 2) a monitoring model development, and 3) capacity development.
-
Output 1: The wide spread mechanisms of multi-drug resistant bacteria in Vietnam are clarified microbiologically, pharmacologically and anthropologically.
-
Output 2: A comprehensive monitoring system for antibiotics residue and antibiotic-resistant bacteria over the process from food production to intake is developed.
-
Output 3: Researchers and technical staff related to food safety monitoring at the targeted research institutes are trained.
In an activity level to produce these outputs, the Project organizes four working groups :1) Microbiology, 2) Pharmacology, 3) Anthroplogy, and 4) Human Resource Development working group (WG). These WGs comprising from Vietnamese and Japanese members engage in following activities at five sites in Vietnam: 1) Hanoi, 2) Thai Binh, 3) Nha Trang, 4) HCMC, and 5) Can Tho.
II. Activities by Working Groups
(1)Microbiology WG: Microbiology deals with micro-organisms such as bacteria and their effects on people. Microbiology WG firstly analyzes whether there are targeted bacteria in human, foods, etc. One of main interests of the WG is whether targeted bacteria found from samples are resistant to particular antibiotics or not. Deeper eyes in a molecular level such as DNA testing are important for the WG so that they can trace or hypothesize how resistant DNA is spreading among samples. Activities in the PDM are followings.
-
1): To isolate ESBL-producing bacteria from specimens obtained from human, environments, foods, livestock and marine products.
-
2): To characterize isolates of ESBL-producing bacteria by antibiotic-resistant phenotype, genotype and plasmid typing.
-
3): To determine the transmission of antibiotic-resistant bacteria /plasmids within a family and community.
-
4): To determine the factors influencing to the stability of antibiotic-resistant bacteria carrier.
-
5): To collect data on antibiotics used in human and agriculture from related Government organizations.
-
6): To analyze microbiological, pharmacological and sociological data epidemiologically by using analysis softwares.
 Chicken sampling
|
 Healthy human sampling
|
 Bacteria isolation
|
 DNA analysis
|
(2)Pharmacology WG: Pharmacology is the branch of chemical science, which deals with drugs or medicines. The WG's main interest is whether antibiotics remain in foods, environemnets, showing what kinds of antibiotics are there and how much they remain in samples. Usining equipment to detect antiboitic residues and develop a quick method or an efficient protocol, their evidence will link with Microbiology WG's findings on antibiotic resistant bacteria as well as Anthropology WG's findings on social contexts. Following activities are the scope of PDM.
-
1): To screen antibiotics in specimens collected from environments, foods, livestock and marine products by microbiological methods.
-
2): To identify antibiotics and related chemicals in specimens by biochemical methods.
 Fish sampling
|
 Sample preparation
|
 Meat treatment
|
 LC-MS/MS analysis
|
(3) Anthropology WG: Anthropology is a social scientifc study about people, society and culture. Going out from laboratory, the WG's fields are where Vietnamese live in such as local communities, households, markets, etc. Focusing on people's behaivour or custom, the WG hypothesizes why antibiotic resistant bacteria or antibotic residues are spreading in terms of social cotexts. Also one of their important missions is to make a model of public health actions to prevent from the spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria in local communities. The PDM activities are as follows.
-
1): To develop an understanding model for the local custom and system on food.
-
2): To develop an understanding model for illness and intake of medicine.
-
3): To analyze the relation between the habit and infection with antibiotic resistant bacteria.
-
4): To develop an intervention model for prevention of the outbreak of multi-drug resistant bacteria at a local community.
 Market interview
|
 Public health study design
|
 Household interview
|
 Women interview
|
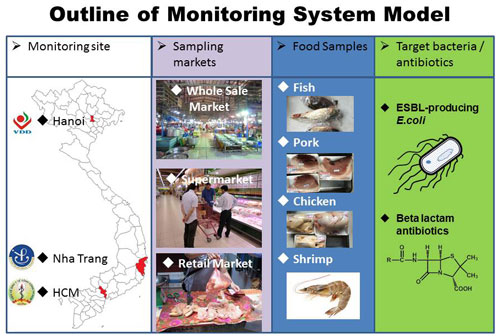
(4) Monitoring activities: Integrating three WGs' knowledge toward a social application, a taskforce of the Project develops a model of monitoring system to watch the prevalence of a drug resistant bacteria and antibiotics residues in foods. Selected markets in several area in Vientam are monitored from microbiological and pharmacological eyes to provide data in a systematic way. The Project develops a practical manual showing a common procedure to operate the monitoring model so that we can propose a compatible or integrated with a national strategy on food safety to government levels. Monitoring activities consist of followings.
-
1): To determine the model sites for development of the monitoring system (selected sites are Hanoi, Nha Trang, and HCMC).
-
2): To prepare a practical manual for comprehensive monitoring system of multi-drug resistant bacteria in the process from food production to intake.
-
3): To verify the effectiveness of the model monitoring system developed.
-
4): To revise the practical manual based on the results of above activity.
 |
 |
(5) Human Resource Development WG: The WG aims at developing capacity of Vietnamese researchers or technicians to keep the future sustainability after the Project. To do this, the WG designs several training courses for researchers in both Vietnam and Japan. Not only academic courses for doctoral or master degrees, but also technical courses for laboratory methods will be organized by the WG. Also the WG's mission is to disseminate the Project's achievements through scientific meetings or open workshops to contribute in solving issues in Vietnam and global context.
-
1): To prepare a training program for researchers and technical staff.
-
2): To train researchers and technical staff according to the program.
-
3): To organize scientific meetings, workshops and advocate to health policy makers for future infection control.
 Doctor course in Japan
|
 Technical training in Japan
|
 |
 Workshop in Vietnam
|





